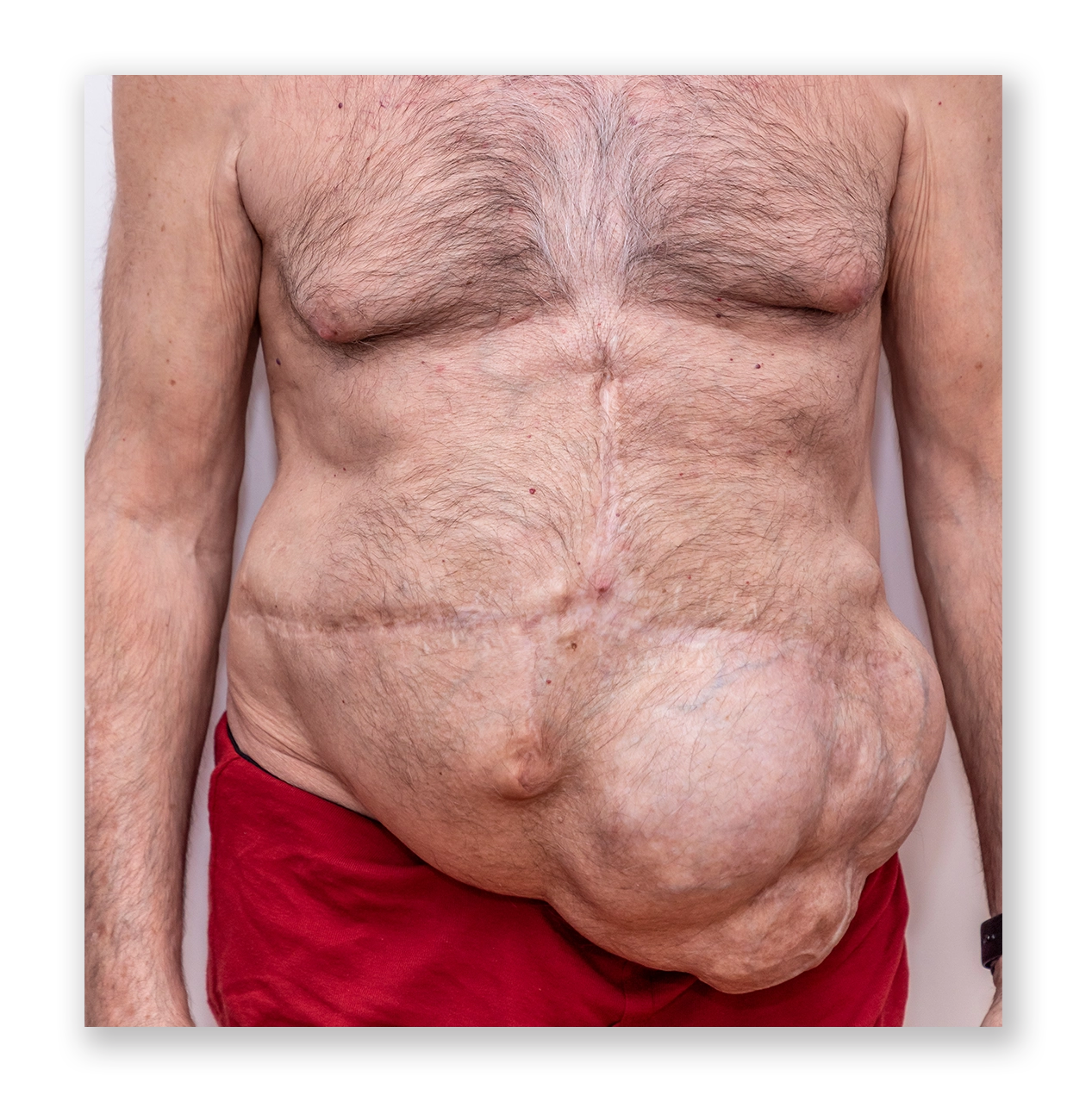
How is it Diagnosed:
A physical exam is often enough to diagnose an incisional hernia, as the bulge is usually visible when the patient stands or strains the abdominal muscles. However, imaging tests such as an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be used to assess the size of the hernia, determine its contents, and help plan the best surgical approach for repair and plan the right of the size of the mesh.
Surgical Approaches to Incisional Hernia Repair
1. Open Hernia Repair
In open surgery, a single, small incision is made over the site of the hernia. The surgeon pushes the herniated tissue back into the abdomen and repairs the defect in the abdominal wall. A mesh is often used to reinforce the area and reduce the chance of recurrence.
Advantages:
- Suitable for large or complex hernias
- Provides excellent visibility and access for the surgeon
- Ideal for patients who may not be good candidates for minimally invasive procedures
2. Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive technique that uses small incisions and a camera (laparoscope) to guide the repair. Special instruments are inserted through these small incisions to repair the hernia, often using mesh to strengthen the abdominal wall.
Advantages:
- Shorter recovery time
- Smaller incisions and less scarring
- Lower risk of infection
- Less postoperative pain and quicker return to normal activities
- Can be technically challenging, requiring specialized skills from the surgeon
3. Robotic-Assisted Hernia Repair
Robotic surgery is another minimally invasive technique similar to laparoscopy, but with the use of robotic arms controlled by the surgeon from a console. This approach allows for more precise movements and improved dexterity, making it ideal for complex hernia repairs.
Advantages:
- Enhanced precision and flexibility in surgery
- Similar benefits to laparoscopic surgery (small incisions, faster recovery)
- Ideal for larger or recurrent hernias
4. Mesh Use in Hernia Repair
Surgical mesh is commonly used in both open and laparoscopic hernia repairs to provide extra reinforcement to the abdominal wall. Mesh helps distribute the tension over a larger area and reduces the risk of the hernia returning. There are different types of mesh available, including synthetic materials and biologic meshes, which are absorbed by the body over time.
Advantages:
- Benefits of mesh: Decreases recurrence rates significantly.
Risks: Mesh-related complications, although rare, can include infection, migration, or rejection.
4. Recovery from Incisional Hernia Surgery
Recovery time varies depending on the surgical approach and the size of the hernia. Generally, patients can expect the following:
Advantages:
- Minimally invasive surgery: A faster recovery, with most patients resuming light activities within 1-2 weeks and full recovery in 4-6 weeks.
4. What are complications of Untreated Incisional Hernia ?
If left untreated, incisional hernias can grow larger and lead to complications such as:
Advantages:
-
Incarceration: When the hernia becomes trapped, causing bowel obstruction.
-
Strangulation: Loss of blood supply to the herniated tissue, which can lead to tissue death, requiring emergency surgery.
Conclusion
Incisional hernias are a common complication of abdominal surgery but can be successfully treated with various surgical approaches. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing complications and ensuring a smooth recovery. If you suspect you have an incisional hernia or are experiencing symptoms, consult with your healthcare provider to discuss the most appropriate treatment options for you.